English / 中文
VBFT Introduction
Version 1.0.0
On March 30th Ontology released the first batch of open-source projects to GitHub. As a next-generation public chain infrastructure platform, Ontology will also introduce a new consensus algorithm VBFT, which is based on verifiable random function (VRF). Below we will introduce Ontology’s latest consensus model and its VBFT consensus algorithm. The VBFT algorithm will also be open-source on GitHub.
VBFT is a new consensus algorithm that combines PoS, VRF (Verifiable Random Function), and BFT. It is the core consensus algorithm of OCE (Ontology Consensus Engine). VBFT can support scalability of consensus groups, through VRF guarantee the randomness and fairness of the consensus population generation, and ensure that state finality can be reached quickly.
Ontology’s core network is composed of two parts:
- Consensus network
The consensus network consists of all consensus nodes responsible for consensus on transaction requests within Ontology, block generation, maintaining the blockchain, and distributing consensus blocks to synchronous node networks.
- Consensus candidate network
The nodes in the candidate network do not participate in consensus but remain synchronized with the consensus network and update to the latest consensus block on the blockchain maintained by them in real time. Candidate networks will also monitor consensus network status, validate consensus blocks, and assist in managing the Ontology network.
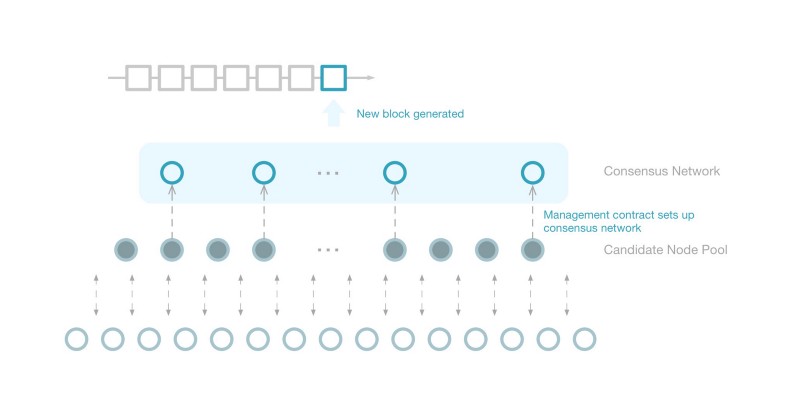
The size of the consensus network is managed through a consensus management smart contract. The stake must be locked for the node in the consensus network (the stake is from the owner of the node).
Ontology Consensus Network Construction
The Ontology consensus network is constructed by the Ontology consensus management smart contract. The consensus management contract runs permanently on the Ontology network and regularly updates the node list in the consensus network and updates the VBFT algorithm configuration parameters in the consensus network.
In VBFT algorithm parameters an important parameter is the PoS table of the consensus network node. During the VBFT operation process, all nodes first randomly select nodes participating in the consensus according to the current consensus PoS table, then randomly selected nodes complete the corresponding round of consensus work.
VBFT algorithm overview
The VBFT algorithm can be considered as an improvement upon the byzantine fault tolerated algorithm from the perspective of verifiable random function. In the VBFT algorithm, first, based on the VRF, consensus candidate nodes are selected in the consensus network, block verification nodes are set, confirmation nodes are set, and then consensus is completed by the selected node set.
Due to the randomness introduced by VRF, the alternative proposal nodes/verification nodes/confirmation nodes of each round are different and difficult to predict, thereby greatly improving resistance against attacks to the consensus algorithm.
The VBFT algorithm can be summarized as follows:
In each round of VBFT consensus,
- Proposal nodes will be selected from the consensus network in accordance with VRF. Each candidate node will independently propose a block;
- Multiple verification nodes are selected from the consensus network in accordance with VRF, and each verification node collects blocks from the network, verifies them, and then votes on the highest priority candidate blocks;
- Multiple confirmation nodes from the consensus network are selected in accordance with VRF, perform verification on the voting results of the above verification nodes, and determine the final consensus results;
- All nodes will receive the consensus result of the confirmation node and start a new round of consensus after a round of consensus confirmation.
VBFT’s VRF
The VRF value of each round of blocks in the current VBFT algorithm is determined by the previous round of consensus blocks. The specific algorithm extracts volatile information from the previous block, calculates the hash, and generates a 1024-bit hash value. This hash value will be taken as the VRF value of the next block.
VBFT’s Peer Choice
The VBFT algorithm verifies the random value after the previous round of consensus and selects the nodes to participate in the new round of consensus in the PoS table. The generation of the PoS table considers the PoS information of the node owner and the governance strategy of the entire consensus network. Although the VRF values themselves can be assumed to be uniformly distributed random values, the random node selection of VBFT still follows consensus network management strategy.
Since the VRF value generated by one block is verifiable, all nodes will be consistent with the VRF of the same block height if there’s no forking. In the VBFT algorithm, for each round, a set of nodes are selected in the PoS table based on the VRF sequentially. Therefore, each VRF value determines a sequence of consensus nodes. This randomly selected node sequence can be taken as one priority order of all consensus nodes.
VBFT’s Fork Choice
Ontology, as a public chain, runs on a public network and faces the possibility of network failure or malicious attacks. Although the VBFT consensus algorithm randomly selects nodes to participate in the consensus and decreases the possibility of network attacks, it still faces the risk of forking in the occurrence of network isolation.
In the previous section, it was explained that the VRF of each block can determine the node sequence. When there is a fork choice in VBFT, VBFT defines the node sequence by sequencing node priority. Based on this priority sequencing, each fork priority weighting can be calculated, and each node selects the suitable fork based on the respective fork priority weighting.
Since each block is determined by VRF’s priority order of the nodes, it is very difficult or impossible to continue maintaining a malicious fork, so the malicious fork will soon die. As a result, the VBFT algorithm also provides fast state finality.
VBFT’s Auto-Configuration
To ensure the network quality of the Ontology consensus network, the Ontology consensus management smart contract will automatically update the node list in the consensus network on a regular basis. In the event of cyber attacks, the consensus management smart contract also support mandatory updating of the node list in the consensus network through stake-based voting.
A new node will be added to the consensus network at the next consensus network update after more stakes are locked for this node and confirming that it meets the performance requirements of the consensus network.
The time span from when the consensus network is updated by the smart contract is in unit of block. After each updated consensus network completes a given number of block consensus, an alternative node proposal for the next block must build a consensus management smart contract transaction and package it into the next proposal block as the first transaction in the block. The corresponding consensus verification node and confirmation node will also verify the proposed node to make sure the consensus management transaction is included in block proposal.
After the consensus is reached in the block containing the consensus management smart contract transaction, each node will automatically execute the consensus management contract, update the consensus node list, and complete the update of the consensus node list.
Performance Comparison
| Consensus mechanism | Application scenario | Performance efficiency | Consensus confirmation time | Consensus confirmation time example | Number of consensus nodes | Tolerated malicious nodes | Resource consumption | Manageability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POW | Public chain | <20tps | High | Bitcoin: 60 minutes Ethereum: 1 minute |
- | 50% | High | Low |
| POS | Public chain | <20tps | High | - | 50% | Medium | Medium | |
| DPOS | Public chain | >500tps | Medium | BitShares: 10 seconds | Less than 30 | Supported | Low | High |
| PBFT | Alliance chain/private chain | >1000tps | Low | FISCO-BCOS: 1 second Fabric: 1 second |
Less than 30 | No more than 1/3 of consensus nodes | Low | High |
| VBFT | Public chain/private chain | >3000tps | Medium | Ontology TestNet: 5-10 seconds | Less than 1,000 | Configurable, no more than 1/3 of consensus nodes | Low | High |
| Paxos/RAFT | Alliance chain/private chain | >5000tps | Low | FISCO-BCOS: 1 second | Less than 30 | Not supported | Low | High |